* On your first PCB Assembly order!
* Up to $300 discount
 C - A L L E Y
C - A L L E Y 
Home | Events | PCB | About Us | News | Contact Us
Before PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) production, Kingsheng PCBA regards Incoming Quality Control (IQC) as the first crucial quality control checkpoint. The primary objective is to ensure that all materials entering production comply with design specifications and quality standards, thereby preventing batch quality problems at the source and avoiding production delays, cost waste, and decreased finished product reliability due to material issues.

Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Process and Methods
Incoming materials for PCBA primarily include Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), electronic components, solder paste, and auxiliary materials (e.g., adhesives, cleaning agents). IQC inspection typically follows below steps:
1. Document Verification:
Confirm consistency between the delivery note and purchase order information, including material codes, specifications, quantities, and production batch numbers.
2. Appearance Inspection:
PCB: Inspect for any defects such as scratches, indentations, exposed copper, blistering, warping, loss of solder mask, poor metalization of holes, etc. This is typically performed using a magnifying glass or AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) equipment.

Components: Inspect whether the packaging model, imprint (logo, value, batch number) is clear and correct. Check pins for oxidation, bending, lifted leads, or damage. For IC-type components, special attention must be paid to the integrity of anti-static packaging.
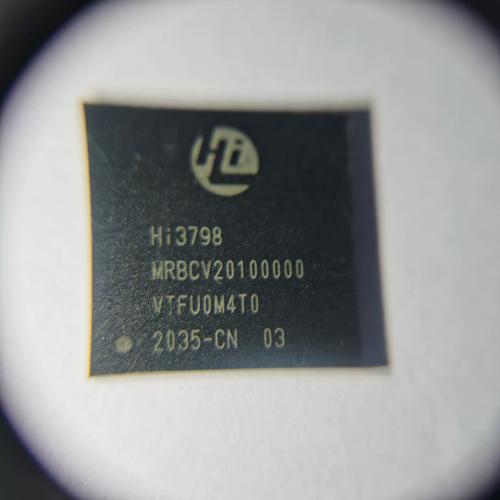
Solder Paste: Inspect the packaging seal integrity, brand and model, and shelf life. Record the warm-up time.
3. Electrical Performance and Dimensional Inspection:
PCB: Perform electrical continuity tests using a flying probe tester or a test fixture to ensure all network connections are correct and accurate, free from short circuits or open circuits. A 2D image measuring instrument is used to inspect critical dimensions, hole diameters, trace widths and spacings, etc., for compliance with Gerber documentation requirements.
Components: For passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, sample measurements are conducted using an LCR meter to verify whether their capacitance, resistance and inductance values fall within the tolerance range. For active components such as ICs, functional tests can be conducted on-site or more complex tests can be entrusted to a third party.
4. Solderability Testing:
Solderability testing is performed on PCB pads and component leads, such as the wetting balance test, to ensure their surfaces have good solderability, preventing defects such as cold solder joints and non-wetting in subsequent production.
5. Record and Identification:
All inspection results must be thoroughly recorded in the Incoming Material Inspection Report. Acceptable products shall be affixed with a "PASS" green label, and warehousing procedures shall be completed.
Rejected Material Handling Procedures
Strict and clear handling procedures must be followed to prevent rejected materials into the production line:
1. Segregation and Identification:
Move immediately rejected materials to the designated "Rejected Area" and remark them.
Affix a "Rejected" red label, indicate material information, rejected reason, quantity, and inspection date.
2. Record and Report:
Clearly record rejected details in the inspection report and immediately submit a "Rejected Report" to the Procurement Department and Quality Manager.
3. Material Review Board (MRB):
Material Review Board (MRB) shall be formed, comprising representatives from the Quality Assurance (QA) Department, Procurement Department, Engineering Department, and Planning Department, to jointly review the rejected materials and decide on the handling solution. Common solutions include:
Return/Replace: For materials with nonconforming key parameters and that are unusable, this is the most common handling method. Procurement contacts the supplier to process return or replacement procedures.
Use As Is (UAI) / Concession Acceptance: For minor defects that do not affect critical product functions, performance, and reliability (e.g., minor cosmetic flaws), concession acceptance may be granted with customer consent. However, the production status of this batch of materials must be strictly tracked.
Sorting/Rework: If only a part of one kind of material are nonconforming, the supplier may be requested or internal personnel may be arranged to perform 100% sorting. Alternatively, the rejected items may be returned to the supplier for sorting/rework (e.g., pin straightening, re-tinning, etc.), and then returned for inspection after qualification.
Scrap: Materials that cannot be reworked, have no usable value, and cannot be returned are processed as scrap, and records are kept.
4.Supplier Feedback & Corrective and Preventive Actions:
The Quality Department provides information of rejected materials to suppliers, requesting them to conduct root cause for analysis and provide a "Corrective and Preventive Actions Report (CAPA)". Based on the effectiveness of the supplier's corrective actions, the inspection stringency for subsequent supplies is adjusted (e.g., increasing the sampling ratio or make full inspection), or even the supplier list is optimized.
Summary:
Rigorous incoming material inspection and efficient non-conforming product handling mechanisms are the foundation for building a high-quality PCBA production system.

For Kingsheng PCBA, incoming material inspection is not only a process of screening out rejected materials but also a key management activity that drives continuous improvement in supply chain quality, reduces overall quality costs, and ensures final product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Please send Email to kspcba@c-alley.com or call us through +86 13828766801 Or submit your inquiry by online form. Please fill out below form and attach your manufacturing files( PCB Gerber files and BOM List) if need quotation. We will contact you shortly.
 +86 13828766801
+86 13828766801 kspcba@c-alley.com
kspcba@c-alley.com https://www.kingshengpcba.com/
https://www.kingshengpcba.com/ 2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108
2/F, Building 6, Tangtou 3rd Industrial Zone, Tangtou Community, Shiyan Town, Baoan District, Shenzhen, China, 518108